When designing your flow station for gas flow measurements, the most common confusion begins with CFM, SCFM, and ACFM. All three have similar definitions, but relay totally different data. Let us explain how.
CFM stands for Cubic Feet per Minute and is normally used to indicate the working capacity of a pump, compressor, or a blower.
ACFM stands for Actual Cubic Feet per Minute and is a unit of volumetric flow rate of a gas displaced by a pump at operating or present conditions of temperature and pressure.
Whereas SCFM is also a unit of volumetric flow rate that stands for Standard Cubic Feet per Minute. SCFM is the measured gas flow with respect to fixed reference operating conditions and is the most useful measure of gas flow. These reference conditions may vary based on industry and geographical region, but commonly used reference conditions are:
(1) Temperature @ 68°F
(2) Pressure @ 14.5 PSIA
The reason experts around the world introduced the concept of measuring gas flow in SCFM is to standardize all gas flow measurements. This is because, the volume a gas occupies is dependent on its temperature and pressure. For example, a fixed mass of air will occupy larger volume at higher temperature and will undergo compression (smaller volume) at higher pressures.
This means person “A” measuring 1 ACFM of air at their operating temperature T1 and pressure P1 is not the same “amount” or “mass” of air as person “B” measuring 1 ACFM of air at a completely different set of operating conditions (temperature T2 and pressure P2).
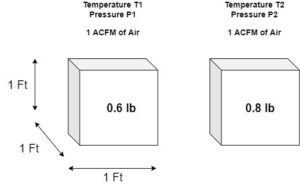
Therefore, when gas readings are obtained in SCFM or “fixed” reference conditions, gas flow measurements will be standardized or remain consistent and will mean the same regardless of the operating conditions.
To obtain gas flow readings in SCFM, firstly, the gas is measured in ACFM at actual and “known” operating conditions. Meaning a continuous temperature and pressure input is required to track actual operating conditions. The flow computer then uses the below mathematic correction factor, or a variation thereof, to convert ACFM to SCFM that utilizes the actual and reference temperature and pressure values:
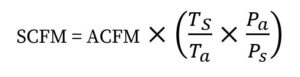
Ts: Standard Temperature
Ps: Standard Pressure
Ta: Actual Temperature
Pa: Actual Pressure
If you would like to speak to an expert about your gas flow application then contact us at sales@seztec.com
Explore our range of gas flow meters
Copyright © 2022 Seztec LLC